
AN4005, a drug candidate discovered in-house, is an oral small-molecule PD-L1 inhibitor designed to disrupt the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1. Compared to the crowded anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies space, small-molecule PD-L1 inhibitors are in early stages of development with no drug yet on the market. Small molecule PD-L1 inhibitors have lower production costs, and shorter half-life that may allow for dose titration and schedule modifications to minimize immune-related adverse events.
In preclinical studies, AN4005 was well tolerated and exhibited tumor growth inhibition (TGI) comparable to FDA-approved anti-PD-L1 antibody. In addition, the anti-tumor activities of AN4005 were demonstrated to be dependent on the immune system.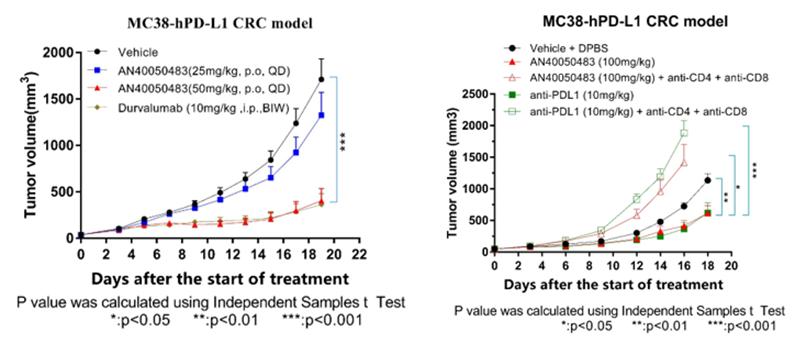
First in Human, Dose Escalation Study of AN4005 (NCT04999384)
AN4005X0101 (NCT04999384) is a Phase I, multi-center, open-label clinical trial study in patients with advanced solid tumors. A traditional ‘3+3’ design was employed for dose escalation, with sentinel patients enrolled at the starting dose of 50 mg BID. As of 14 October 2024, 25 patients with advanced solid tumors in the U.S. and China received AN4005 across six tested dose levels (50 mg BID to 1000 mg QD).
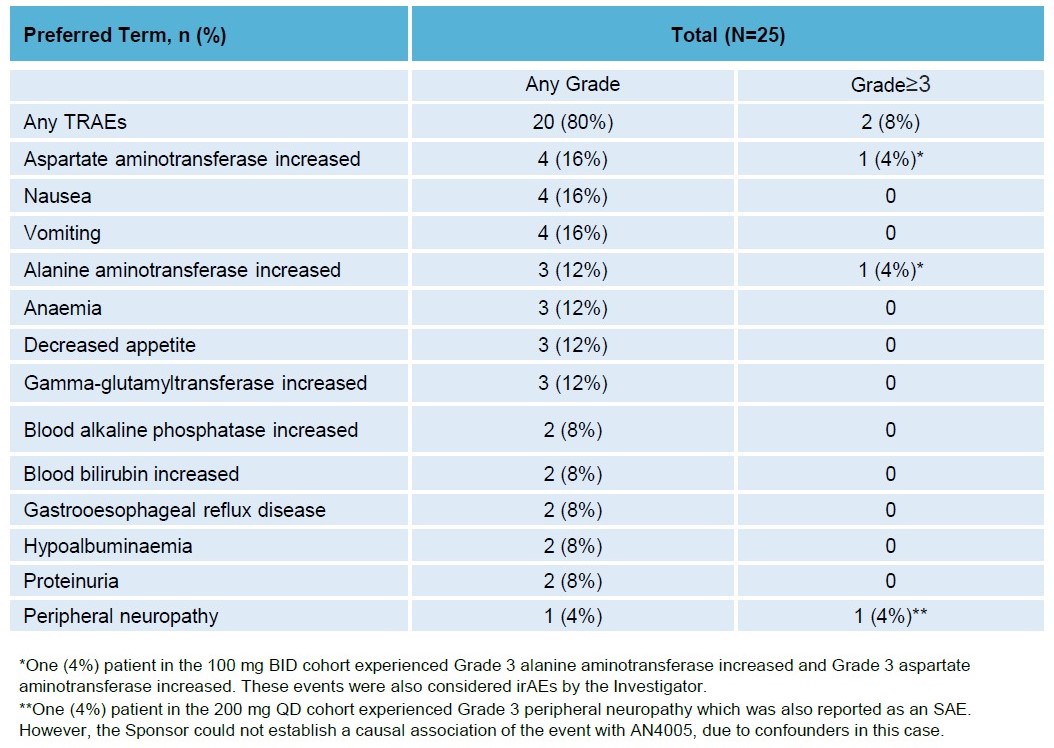
AN4005 was well-tolerated with 20 (80%) patients experienced at least one AN4005-related AE, two (8%) patients experienced Grade 3 AN4005-related AE. No Grade 4 or 5 AN4005-related AEs were observed. 8 (32%) patients experienced 15 serious adverse events (SAEs); 1 (4%) patient experienced 1 SAE assessed by investigator as related to AN4005. Immune-related AEs were reported in two patients (8.3%) and manageable. No patients experienced AEs leading to dose reduction of AN4005. 9 (36%) patients experienced at least 1 AE leading to dose interruption of AN4005. 4 (16%) patients had AE that led to discontinuation of AN4005. No dose-limiting toxicities were observed and the MTD was not reached.
Treatment-Related Adverse Events (TRAEs) Reported in≥2 Patients with any Grade or in≥1 Patient with Grade≥3
Overall disease control rate was 41.7% (10/24). One patient with high microsatellite instability (MSI-H) colorectal cancer treated at 300 mg QD had a confirmed complete response. Notably, this patient had responded to two prior anti-PD-(L)1 mAbs but was unable to continue intravenous therapy due to the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting the value of an oral PD-L1 inhibitor. Following the completion of the Dose-Escalation Phase and a preliminary food-effect cohort, the trial has now advanced to the Expansion Phase, evaluating two doses of AN4005 in checkpoint inhibitor-naïve patients. Proof-of-concept data from the Expansion Phase is expected to be presented in a conference in 2026.
Reference
1. A Phase I study of AN4005, an orally available PD-L1 inhibitor, in patients with advanced tumors: safety and preliminary efficacy, SITC 2024 (pdf)